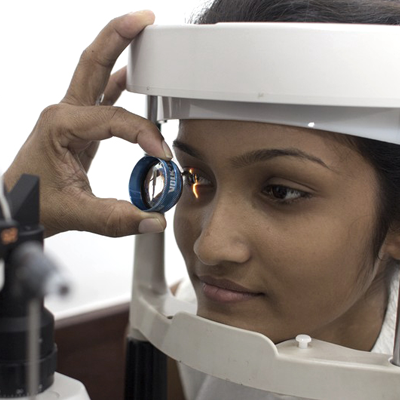
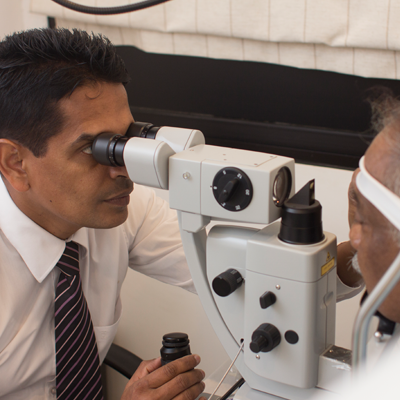
The refraction test is an eye exam that measures how the light is bent and focused on the nerve layer (retina) in the eye. If the image is properly focused on the retina the refraction test becomes zero or Plano and the vision should read as 6/6 ( the line a normal person should read at a distance of 6 meters. )
If the image is not focused properly on the retina then we call it as a refractive error. Then the vision becomes less than 6/6.
The refraction test is done to focus this image back on the retina and gives the power of lenses needed to correct it as a prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
There are four basic refractive errors namely,
Astigmatism (abnormally curved cornea causing blurred vision)
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
Myopia (nearsightedness)
Presbyopia (inability to focus on near objects that develops with age)
If the vision can not be improved to the normal values following a refraction test may be due to a complex refractive error ( keratoconus) , some other pathology within the eye ( cataract ) or due to non ocular cause ( stroke).
Please discuss with the doctor for the reason Where your refraction test does not make your vision normal.